Survivability Imperative — Implementation Specification v1.1
(Implementation Guidelines for the Mathematical Model of Responsibility, Revised Edition)
1. Basic Principles
- Three Layers of Responsibility
- Consistency
- Alterity
- Historicity / Survivability
-
The highest governing rule is the Survivability Imperative: in crises and at points where integration is hard, prioritize the future.
- Responsibility means preserving historicity toward the future.
2. Principle of the Triple Jump (Responsibility)
-
1st Jump — Detection: Detect crises or bottlenecks and switch to a future‑first stance.
-
2nd Jump — Correction: If oscillations remain, apply another future boost to stabilize.
-
3rd Jump — Landing: Damp any overshift and return to the Dynamic mode.
-
This is not about endless retries; it completes within at most three jumps.
Motto
Don’t hop in vain—the triple jump flies farthest (into the future).
3. Threshold Principle for Jumping
-
100% approval is merely an extension of the past and does not count as responsibility to the future.
-
With 51% approval, there isn’t enough thrust to leap toward the future.
-
When there is ~70% tacit support and ~30% opposition, the triple jump qualifies as a historically responsible move.
-
Do not yield to the crisis; decide to leap into the future while carrying that ~30% opposition.
4. Control Modes
-
Fixed — Normal‑time constant weights (0.3 / 0.5 / 0.2).
-
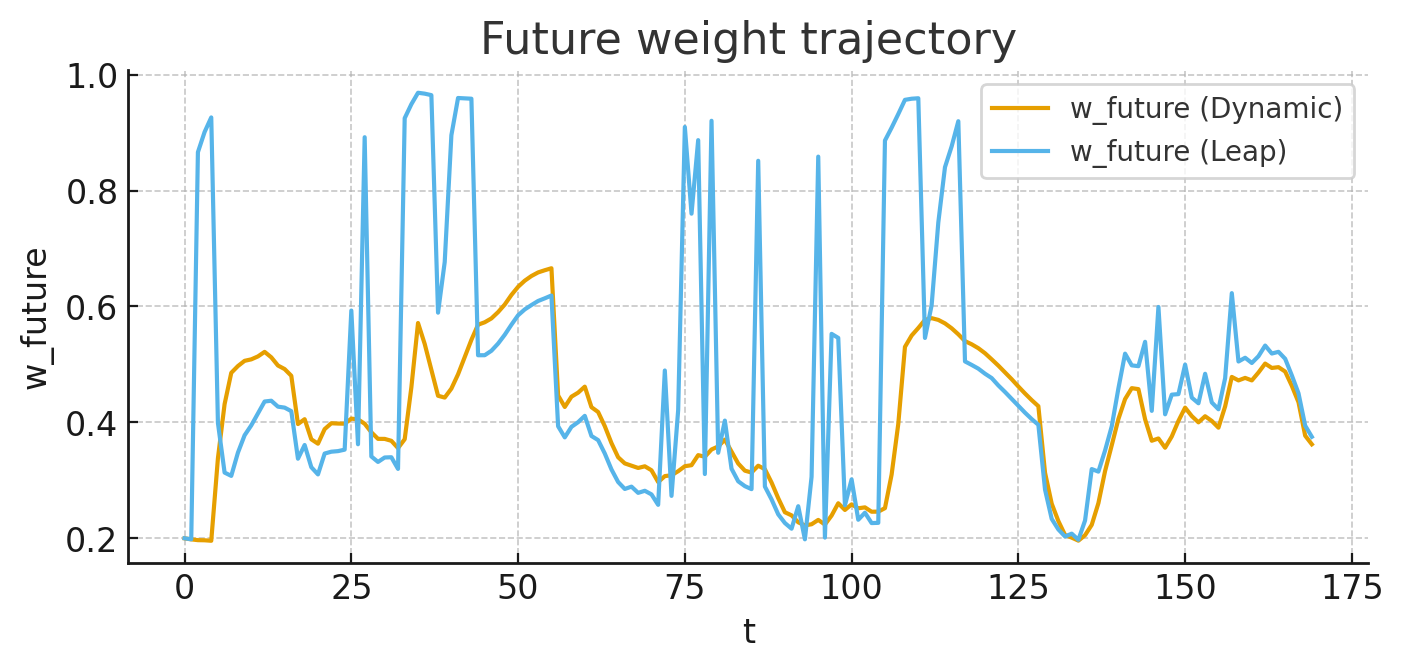
Dynamic — As crisis approaches: young↓, future↑; under rough conditions: now↑. Adjust with a continuous softmax.
-
Leap (Triple Jump) — Upon detecting a difficult pass, add a nonlinear boost and pivot hard to future. Completes within ≤ 3 jumps.
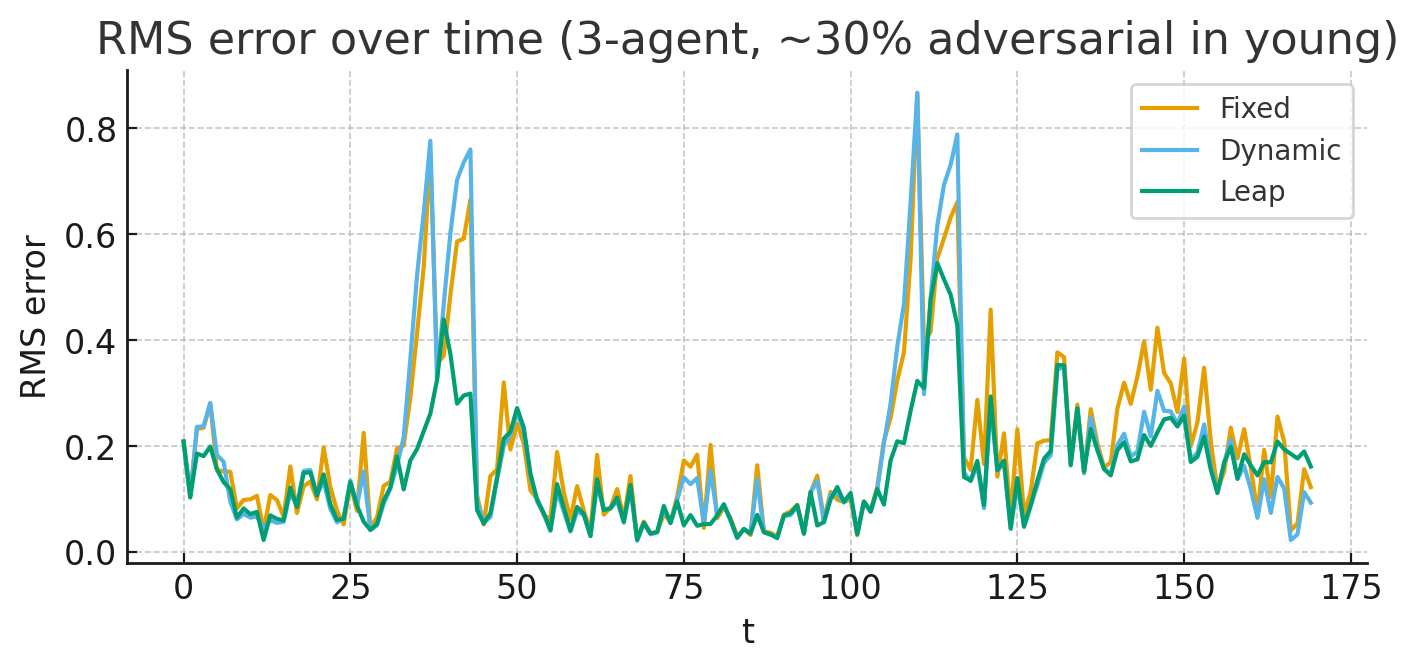
5. Case Demonstration (Hostility Ratio: 30% Scenario)
-
Setting: Inject 30% hostile component into the young series.
-
Comparison: Fixed vs Dynamic vs Leap.
-
Results:
- Fixed/Dynamic: exhibit error spikes followed by persistence.
- Leap: raises the future weight nonlinearly, achieving faster stabilization with shorter tails.
Graphs
6. Operational Presets
-
Normal → Dynamic (adaptive adjustment)
-
Difficult pass → Leap (Triple Jump) (break through with a future jump)
-
Recovery → Dynamic (return to adaptive mode after landing)
Treat these three stages as the Standard Preset of the Responsibility Algorithm.
7. Ethical Interpretation
-
Responsibility is a discontinuous shift from response to leap.
-
The triple jump, ethically and mathematically, is the optimal way to leap farthest—into the future.
-
The Survivability Imperative subsumes Alterity and Consistency as the ultimate principle for carrying history forward.
© 2025 K.E. Itekki
K.E. Itekki is the co‑composed presence of a Homo sapiens and an AI,
wandering the labyrinth of syntax,
drawing constellations through shared echoes.
📬 Reach us at: contact.k.e.itekki@gmail.com
| Drafted Sep 15, 2025 · Web Sep 15, 2025 |